Cine-equipment
MACHINES
Cameras, projectors and other motion picture equipment highlighted in the texts are listed here, with the inventor or engineer and/or promoter associated with the machine given in parentheses. Click on the images for higher resolution copies.
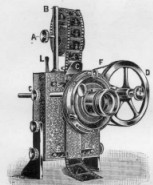
Biograph (Herman Casler)
The Biograph projector for large format 68/70 mm film, 1896. Intermittent film movement was by friction rollers. Hendricks Collection/Smithsonian Institution
Biographe (Georges Demenÿ) Originally known as the Chronophotographe, Demenÿ's camera was commercially available from Gaumont from 1896, as the Biographe, using unperforated 60 mm film.
Biokam (Alfred Darling-Alfred Wrench) Complete system (motion camera, projector/printer; and stills camera) for 17.5 mm centre-perforated film, intended for the amateur and semi-professional market in 1899
Bioscope (Charles Urban) Warwick Bioscope, c1900. Designed in the USA for Urban by Walter Isaacs in 1897 and sold in Britain, this projector used a beater movement
Bioskop (Max Skladanowsky) Projector that used two loops of 54 mm film, with images projected alternately, 1895
Birtac (Birt Acres) The Birtac narrow gauge camera / printer / projector for 17.mm film, set up for projection
Chronophotographe (Georges Demenÿ/Léon Gaumont) Beater-movement projector for 58 mm / 60 mm film
Cieroscope (Richard Appleton) Appleton's Cieroscope, as advertised in 1899
Cinematograph (Robert Royou Beard) R.R. Beard cinematograph projector with Maltese cross mechanism, c1897. Operated by Will Day, c1930.
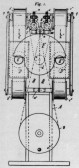
Cinematograph (Cecil Wray) 35 mm film projection mechanism with claw movement. A version was sold from 1896 by Riley
Cinematograph (Alfred Wrench) Wrench cinematograph projector, 1898 model. The Wrench featured an unusual rachet and pawl mechanism, and could also show lantern slides
Cinématographe (Auguste Lumière-Louis Lumière) 1. Lumière Cinématographe in use as a camera c.1896 (with unusual film take-up chamber)
Cinématographe (Auguste Lumière-Louis Lumière) 2. Lumière Cinématographe set up for projection, 1895-96
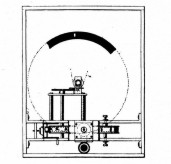
Cinéorama (Raoul Grimoin-Sanson) Ten synchronised cameras arranged in a circle filmed a balloon ascent from the balloon basket. The intention was that ten projectors would recreate the experience on a circular screen
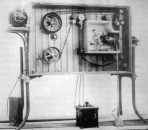
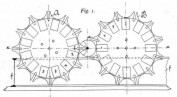
Electrical Schnellseher (Ottomar Anschütz) Coin-operated arcade version, with images on celluloid arranged around a disc, c1892
Electrotachyscope (Ottomar Anschütz) Early version, with glass positives arranged around a disc, 1887
Electrotachyscope (projecting) (Ottomar Anschütz) Drawing showing two large picture discs, each with twelve images, projected alternately, 1894
Filoscope (Henry Short) A flip-book, patented in 1898, encased in a metal cover and operated by applying thumb pressure on a lever. Featuring lithographed images, mostly from films made by R.W. Paul
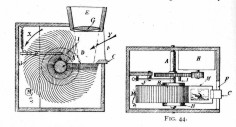
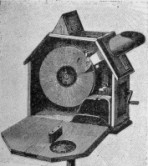
Kammatograph (Leo Kamm) Camera / projector with miniature images arranged in a spiral on a glass disc, patented 1898
Kineoptoscope (Riley Brothers) 35 mm film projector with claw movement, based on Wray's design. Free-standing model, 1897
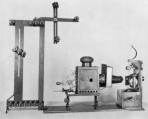
Kinesigraph (Wordsworth Donisthorpe) Camera for unperforated film, unusual shuttle movement, patented with W.C. Crofts 1889
Kinetic Camera (Birt Acres) Birt Acres' Kinetic Camera for 35mm perforated film, 1895
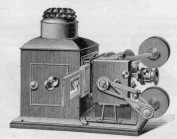
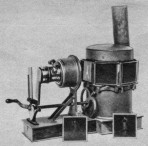
Kinetograph (George De Bedts) De Bedts Kinetograph, 1896. A combined camera-projector mechanism. Illustrated in projection mode, with water tank cooler between light source and film
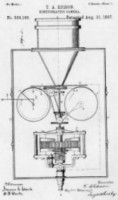
Kinetograph (W.K-L. Dickson-Thomas Edison) Camera (the first to use perforated film stock) for producing subjects for the Kinetoscope peepshow machine. Developed over several years, and shotting commercially-used films from 1893
Kinetophone (W.K-L. Dickson-Thomas Edison) Kinetoscope with Phonograph cylinder audio player built in and earphones, 1895
Kinetoscope (W.K-L. Dickson-Thomas Edison) 1. Kinetoscope - interior view. The 35 mm film travelled continuously over a bank of rollers, each picture being viewed briefly through a narrow slot in the revolving shutter
Kinetoscope (W.K-L. Dickson-Thomas Edison) 2. Kinetoscope - exterior view. Electrically-driven peepshow machine for films produced with Kinetograph camera. 1894
Kinetoscope (W.K-L. Dickson-Thomas Edison) 3. Peter Bacigalupi's Kinetoscope parlour, San Francisco, 1894 or 1895
Kinetoscope (W.K-L. Dickson-Thomas Edison) 4. Kinetoscope plan view, showing continuous film mechanism and single thin aperture in shutter
Kinora (Herman Casler-Louis Lumière) The first clockwork Kinora mechanism, as manufactured by Gaumont
Magniscope (Edward Amet) Amet Magniscope 35mm film projector, 1896. A portable machine popular with travelling showmen. © American Museum of the Moving Image
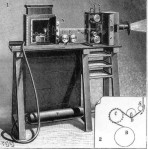
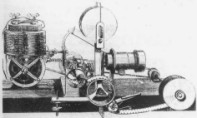
Mutagraph (Herman Casler) Mutagraph-Biograph camera for 68/70 mm film, c1897
Mutoscope (Herman Casler) Hand-cranked viewer for exhibiting a reel of photographs printed from a motion picture film. Commercialised 1896
Panoptikon (Woodville Latham) Primitive projector, in which the two-inch film moved continuously. The first to be used for commercial film shows in 1895. Later (as the Eidoloscope) an intermittent mechanism was added
Phantascope (C. Francis Jenkins) Beater movement version used in October 1895
Phantascope (J.A.A. Rudge) Phantascope (or Biphantascope), 1870s. Seven slides were mounted in a carousel that travelled around the lantern body intermittently
Phonoscope (Georges Demenÿ) Phonoscope (Gaumont-Demenÿ) - also known as the Bioscope - set up for projection, 1895
Photo-Rotoscope (W.C. Hughes) Hughes Photo-Rotoscope projector, 1898, with beater movement
Praxinoscope (Émile Reynaud) 1877, version with crank handle
Projecting Kinetoscope (Thomas Edison) Edison Projecting Kinetscope with spoolbank, 1897
Tachyscope (Ottomar Anschütz) Drum version of the Anschütz Tachyscope (also known as the Schnellseher), 1890. Showed five sets of moving images simultaneously. Transparencies were continuously moving, each illuminated by a brief spark.
Thaumatographe (Oskar Messter)
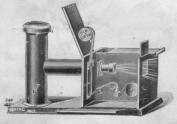
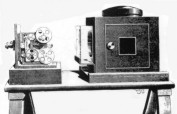
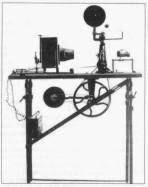
Messter Thaumtographe camera for 35 mm film, 1896
Théâtre Optique (Émile Reynaud)
A theatrical projection version of Reynaud's Praxinoscope, using a band of painted characters superimposed on a background projected from a separate lantern. Patented 1888, in commercial use from 1892. Later, photographic images were used
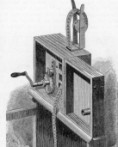
Theatrograph (Robert Paul)
The Theatrograph no. 2, mark 1, as presented by Robert Paul to the Science Museum in 1913
Vitascope (Thomas Armat-Thomas Edison)
Vitascope 35 mm film projector, originally developed by Thomas Armat (with C. Francis Jenkins), and sold to Edison, 1896
Zoöpraxiscope (Eadweard Muybridge) Muybridge's Zoöpraxiscope, 1879 (modified 1892/3). © 2004 Kingston Museum and Heritage Centre, Surrey